| Catalog Number | Size | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLD0702 | 0.5 mL | ¥500.0 | |
| FLD0702-1 | 1 mL | ¥900.0 |
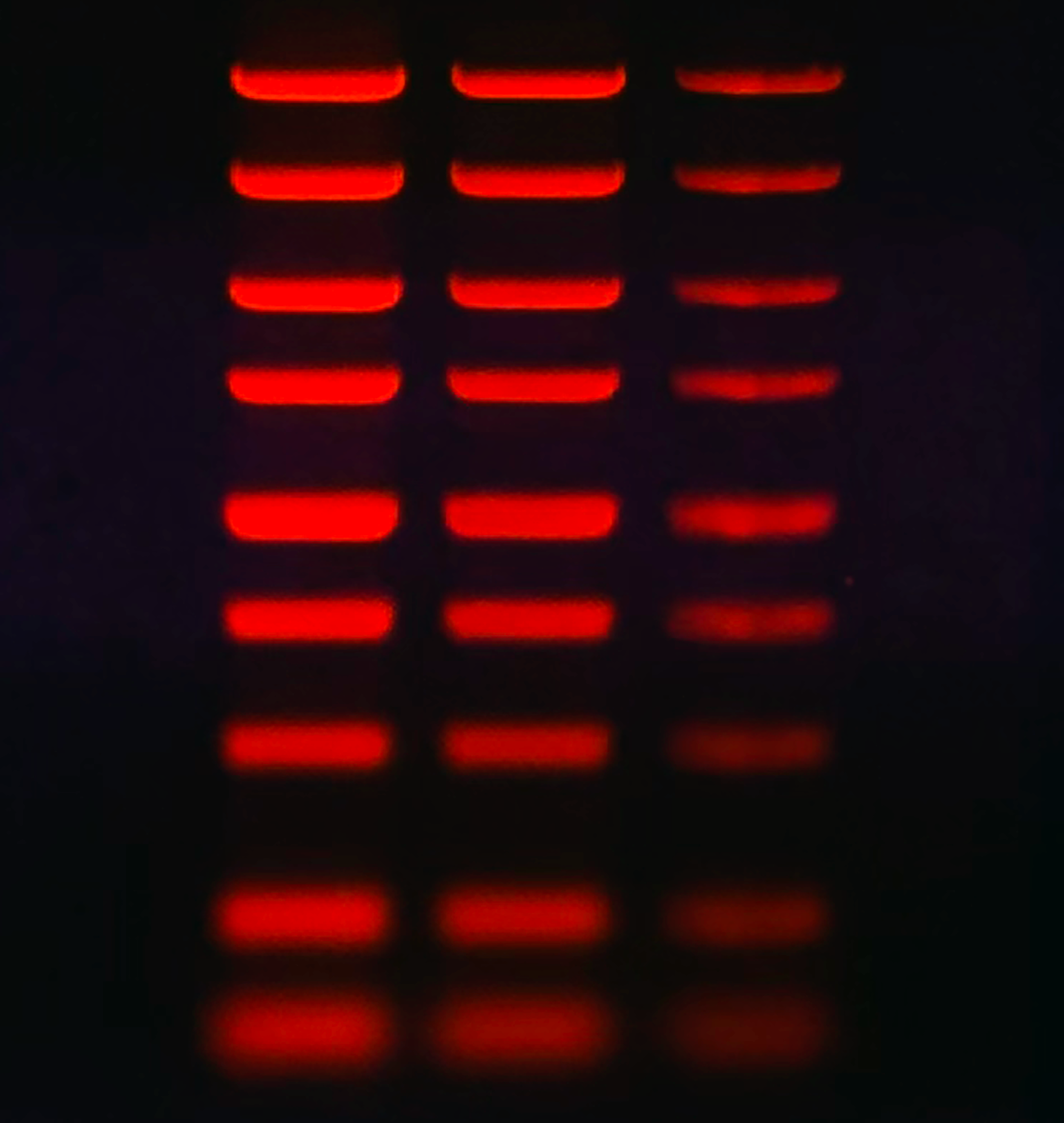
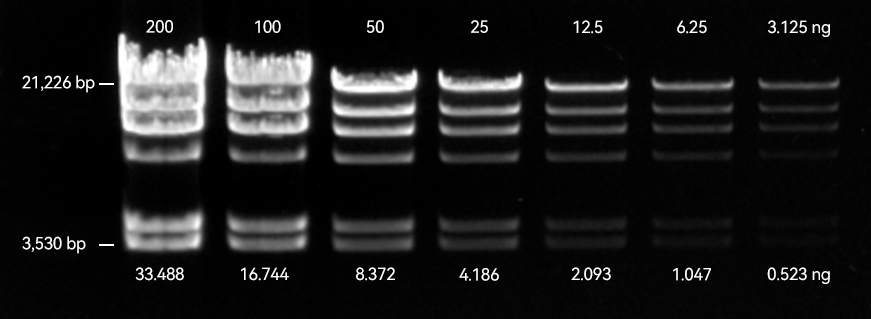
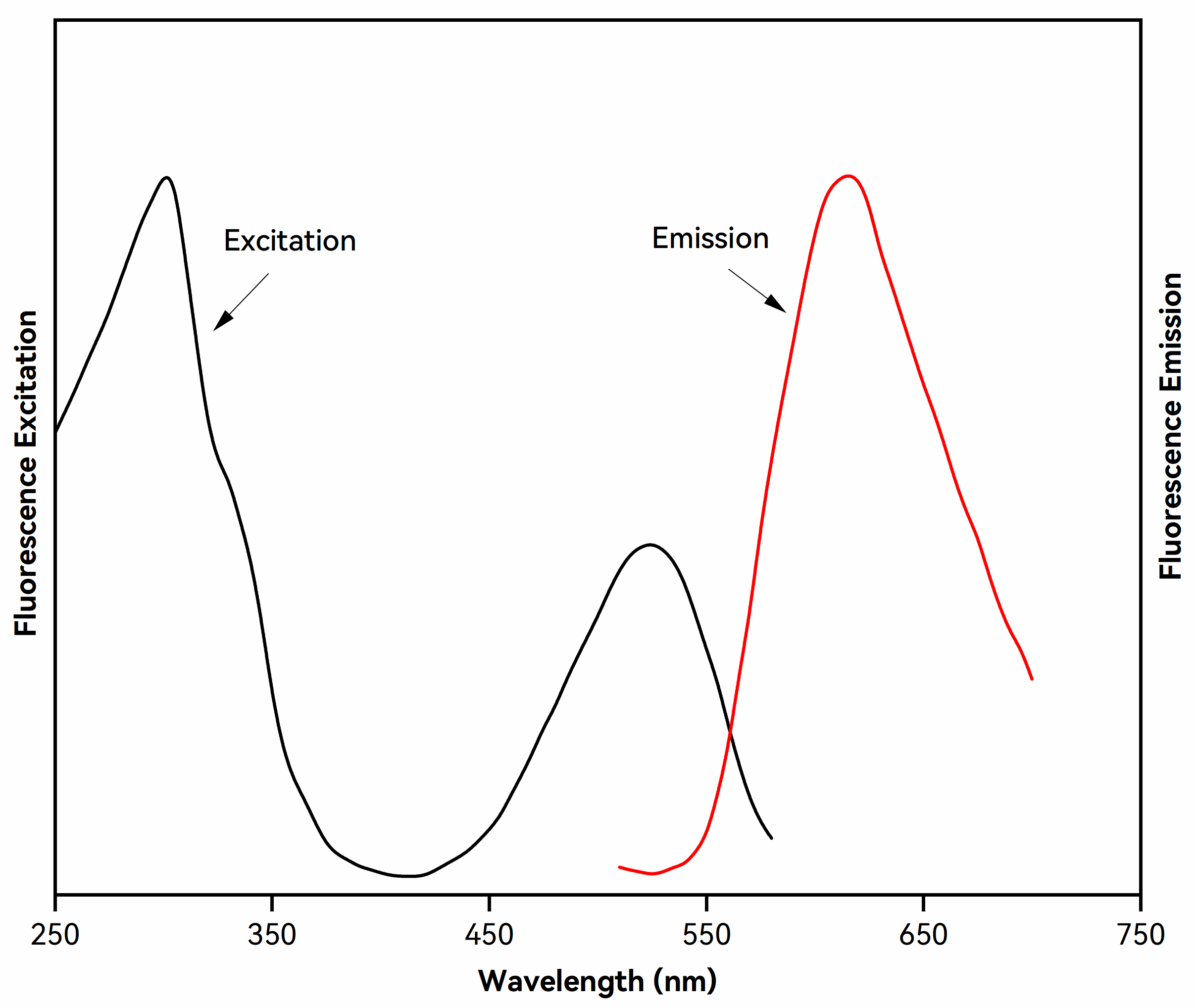
JellyRed is a red fluorescent nucleic acid gel stain, characterized by extremely low cytotoxicity and mutagenicity, along with high sensitivity. It is designed as a safer and more sensitive alternative to traditional ethidium bromide (EtBr) dye for detecting dsDNA, ssDNA, and RNA in agarose or polyacrylamide gels. Its excitation and emission spectra closely match those of ethidium bromide (EtBr), allowing direct visualization with standard UV imaging systems. JellyRed supports both in-gel staining (precast method) and post-staining, and is fully compatible with downstream applications, including gel purification, restriction digest, sequencing, and cloning.



| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Smearing or trailing of DNA bands in pre-stained gels | 1. Reduce the DNA loading amount to 1/2 or 1/3 of the original. JellyRed is significantly more sensitive than ethidium bromide (EtBr), and overloading may cause overexposure or smearing of bands. |
| 2. Consider switching to post-staining instead of pre-staining. Post-staining minimizes interference with DNA migration and improves imaging quality. | |
| 3. For high molecular weight DNA, use a lower percentage agarose gel. Smearing is more common with large DNA fragments. | |
| 4. Use TBE buffer instead of TAE. TBE provides stronger buffering capacity and is better suited for high-resolution electrophoresis. | |
| 5. Avoid using loading buffers containing SDS, as SDS can disrupt dye–DNA binding and alter migration patterns. If SDS is required, post-staining is strongly recommended for optimal results. | |
| Altered DNA migration in pre-stained gels | 1. Reduce the DNA loading amount to 1/2 or 1/3 of the original. |
| 2. Lower the dye concentration; a 0.5× working concentration is recommended for in-gel staining. | |
| 3. Use post-staining instead of pre-staining to minimize interference with DNA migration and improve band resolution and imaging quality. | |
| Reduced fluorescence intensity | 1. The dye may have precipitated. Warm the solution at 40–50 °C for 1–2 minutes and vortex thoroughly to redissolve. |
| 2. Store the dye at room temperature and protect it from light to prevent precipitation caused by low temperatures. |
